Configure client credential authentication for service users
This guide demonstrates how developers can leverage Client Credential authentication to secure communication between service users and client applications within ZITADEL.
In ZITADEL, the Client Credentials Flow can be used for this non-interactive authentication as alternative to the JWT profile authentication.
Steps to authenticate a Service User with client credentials
1. Create a Service User with a client secret
- Navigate to Service Users
- Click on New
- Enter a username and a display name
- Click on Create
- Open Actions in the top right corner and click on Generate Client Secret
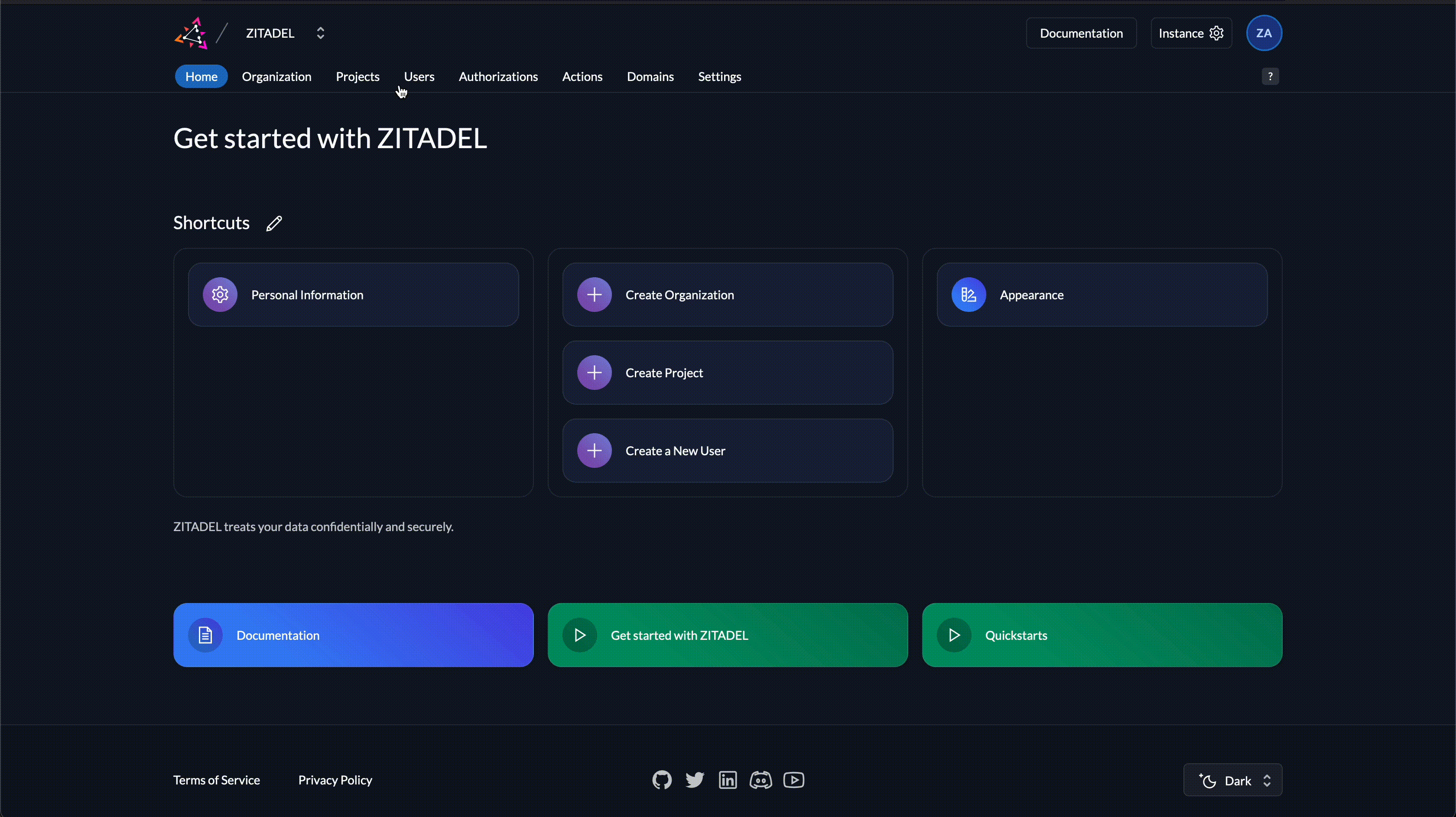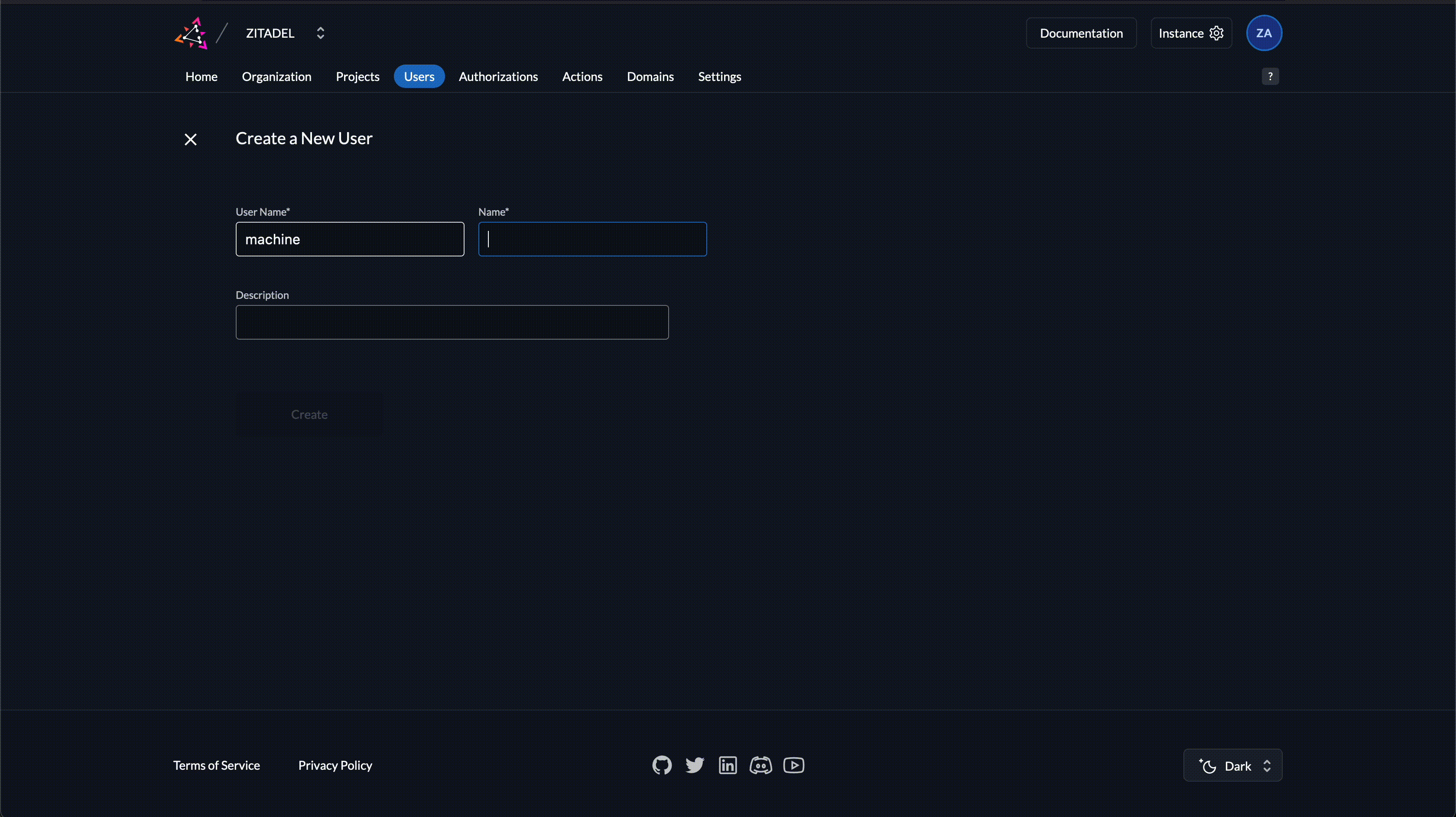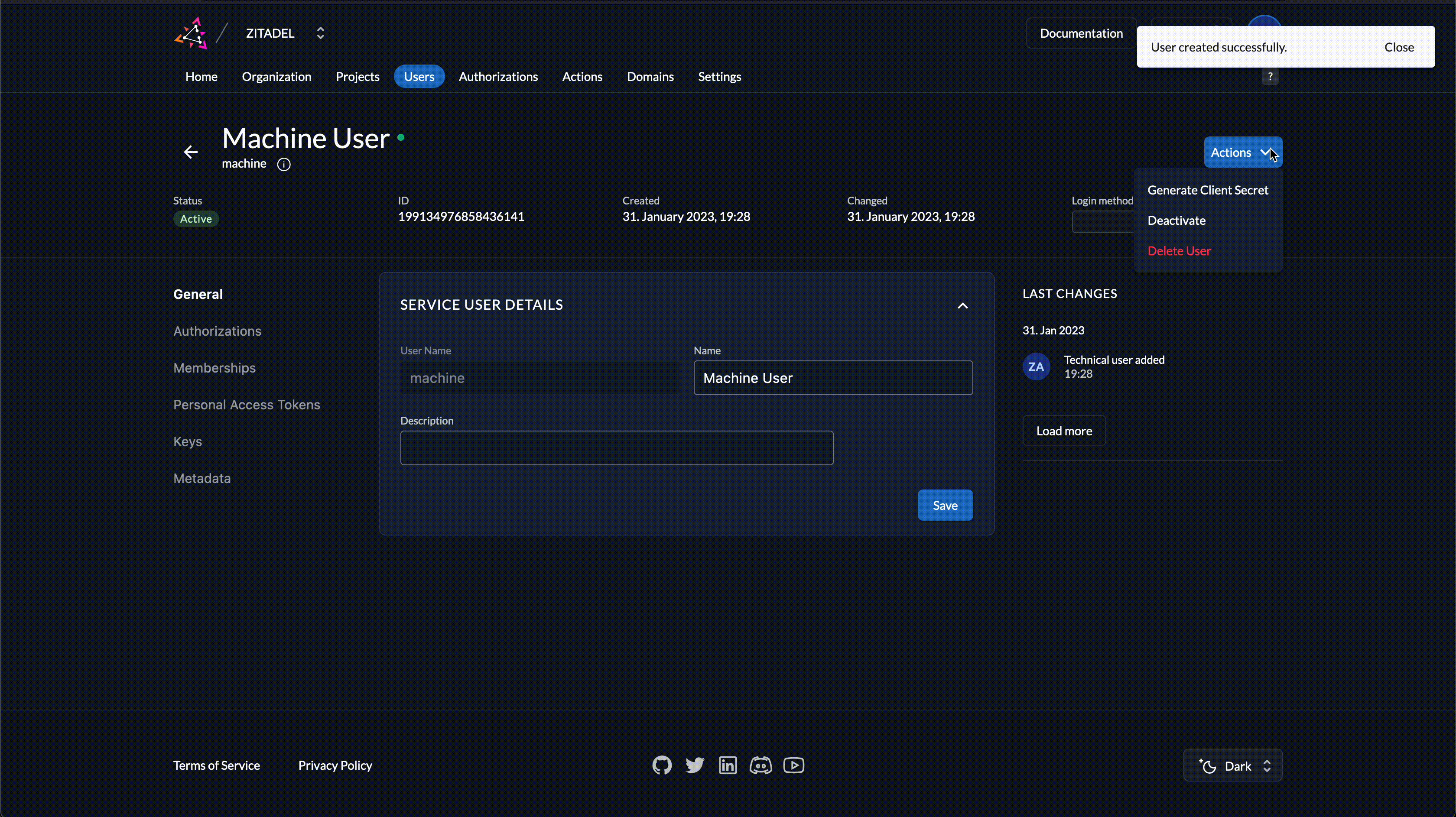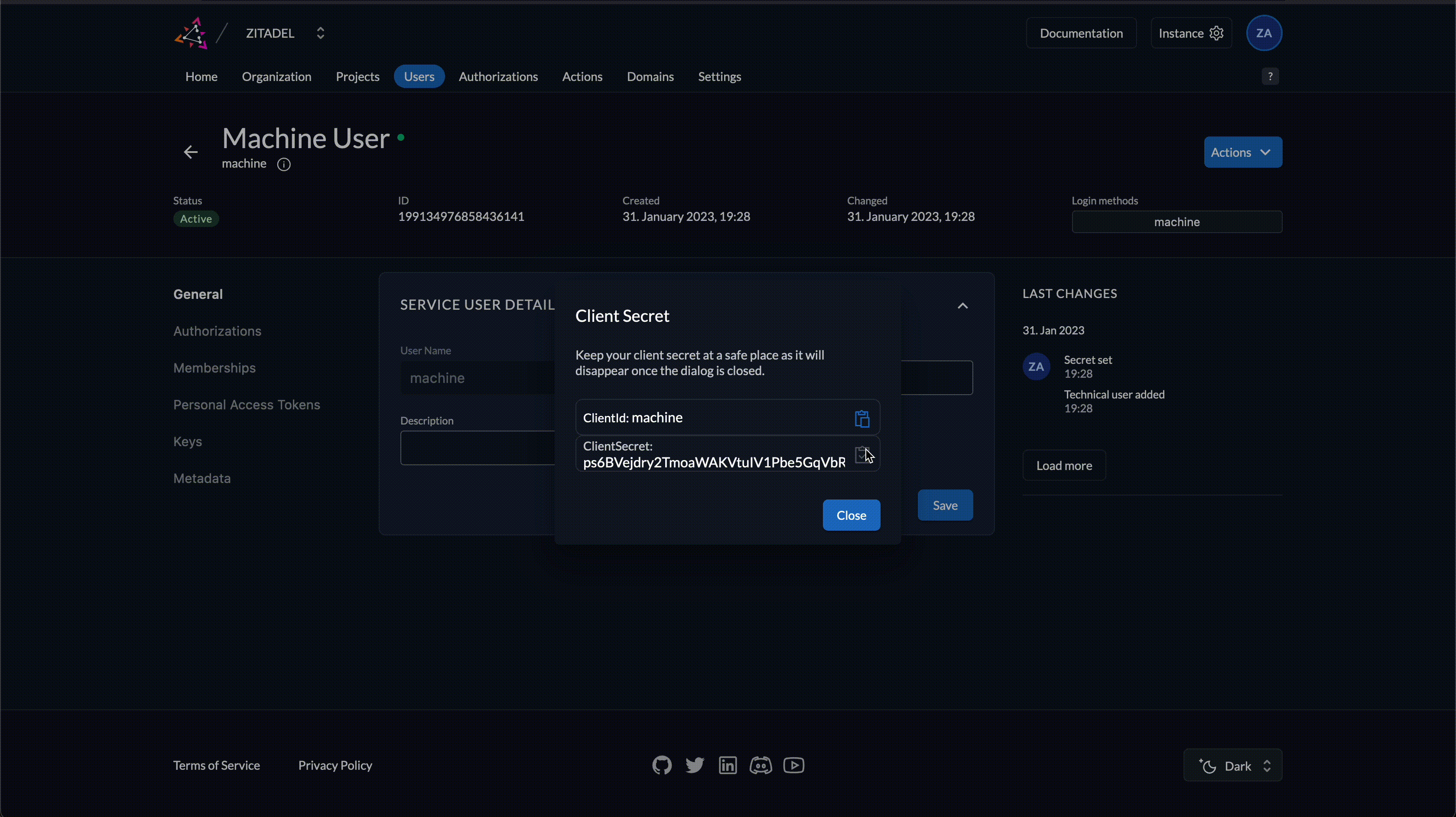
- Copy the ClientID and ClientSecret from the dialog
Make sure to copy in particular the ClientSecret. You won't be able to retrieve it again. If you lose it, you will have to generate a new one.
2. Authenticating a service user and request a token
In this step, we will authenticate a service user and receive an access_token to use against the ZITADEL API.
You will need to craft a POST request to ZITADEL's token endpoint:
curl --request POST \
--url https://$CUSTOM-DOMAIN/oauth/v2/token \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--data grant_type=client_credentials \
--data scope='openid profile' \
--user "$CLIENT_ID:$CLIENT_SECRET"
CUSTOM_DOMAINshould be set to your custom domaingrant_typeshould be set toclient_credentialsscopeshould contain any Scopes you want to include, but must includeopenid. For this example, please includeprofileCLIENT_IDandCLIENT_SECRETshould be set with the values shown in Console when generating a new secret to enable basic authentication
If you want to access ZITADEL APIs, make sure to include the required scopes urn:zitadel:iam:org:project:id:zitadel:aud.
Read our guide how to access ZITADEL APIs to learn more.
You should receive a successful response with access_token, token_type and time to expiry in seconds as expires_in.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
{
"access_token": "MtjHodGy4zxKylDOhg6kW90WeEQs2q...",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 43199
}
Per default a service user will get an opaque access token. If you want to get a Jason Web Token (JWT) as an access token for your user, you can change the token type in the general settings of your service account. To learn more about opaque and JWT tokens read our Opaque Tokens in ZITADEL: Enhancing Application Security Guide
3. Include the access token in the authorization header
When making API requests on behalf of the service user, include the generated token in the "Authorization" header with the "Bearer" prefix.
curl --request POST \
--url $YOUR_API_ENDOINT \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer MtjHodGy4zxKylDOhg6kW90WeEQs2q...'
Accessing ZITADEL APIs
You might want to access ZITADEL APIs to manage resources, such as users, or to validate tokens sent to your backend service. Follow our guides on how to access ZITADEL API to use the ZITADEL APIs with your service user using client credentials.
Token introspection
Your API endpoint might receive tokens from users and need to validate the token with ZITADEL. In this case, your API needs to authenticate with ZITADEL and then do a token introspection. Follow our guide on token introspection with client credentials to learn more.
Security considerations
- Store private keys securely: Never share or embed the private key in your code or application. Consider using secure key management solutions.
- Set appropriate expiration times: Limit the validity period of tokens to minimize the impact of potential compromise.
By following these steps and adhering to security best practices, you can effectively secure service user and client application communication within ZITADEL using client credential authentication.
Notes
- Read about the different methods to authenticate service users
- Service User API reference
- OIDC client secret basic authentication method reference
- Access ZITADEL APIs
- Validate access tokens with token introspection with basic auth